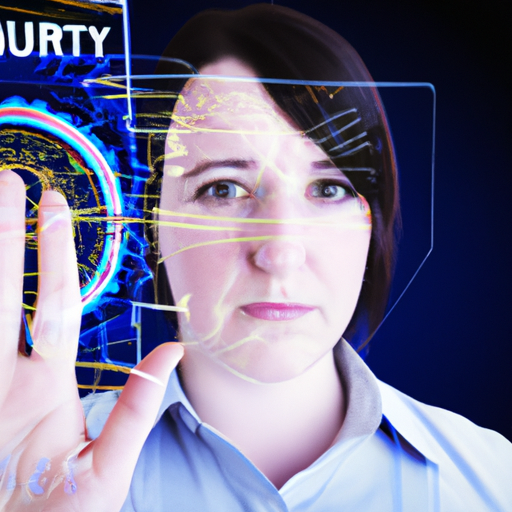
In today’s digital age, the demand for secure authentication methods is at an all-time high. Traditional passwords are becoming a relic of the past, and organizations are looking toward advanced technologies to protect sensitive information. Biometric security stands out as one of the most promising solutions. In this article, we’ll explore what biometric security is, its applications, and how it is shaping the future of secure authentication.
What is Biometric Security?
Biometric security refers to the use of unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, iris patterns, and voice recognition, to verify an individual’s identity. These traits are notoriously difficult to replicate, making biometric methods far more secure than traditional authentication methods.
Types of Biometric Security
- Fingerprint Recognition: This is one of the most widely used biometric methods. Sensors capture an image of a person’s fingerprint and compare it to a stored template.
- Facial Recognition: By analyzing facial features, this technology can identify an individual with high accuracy. It is extensively used in smartphones and security surveillance.
- Iris Recognition: The unique patterns in the iris are captured and analyzed, providing a highly reliable form of biometric identification.
- Voice Recognition: This technology uses the voice’s unique patterns to authenticate users, commonly seen in virtual assistants and customer service applications.
Applications of Biometric Security
Biometric authentication is becoming increasingly prevalent across various industries:
- Banking and Finance: Financial institutions use biometric security to authorize transactions and access accounts, significantly reducing fraud.
- Smartphones: Most modern smartphones are equipped with fingerprint sensors or facial recognition systems, enhancing device security for users.
- Law Enforcement: Law enforcement agencies utilize biometric databases for criminal identification and tracking.
- Workplace Security: Access control systems in organizations rely on biometrics for securing sensitive areas and information.
The Advantages of Biometric Security
Biometric security offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Biometric traits are unique to each individual, making it virtually impossible to forge or steal.
- User Convenience: Biometric methods eliminate the need for remembering passwords or carrying access cards.
- Faster Authentication: Biometric systems provide quick access, reducing wait times for users.
Challenges of Biometric Security
Despite its advantages, biometric security is not without its challenges:
- Privacy Concerns: The collection and storage of biometric data raise concerns about privacy and data breaches.
- False Acceptance and Rejection Rates: No biometric system is perfect, and there can be instances of unauthorized access or valid users being denied.
- Implementation Costs: The initial setup and maintenance of biometric systems can be costly for organizations.
The Future of Biometric Security
As technology continues to evolve, the future of biometric security looks promising. Innovations such as multi-modal biometrics, which combine different biometric traits, promise to enhance reliability and security. Furthermore, advancements in AI and machine learning are expected to improve the accuracy of biometric recognition systems.
Conclusion
Biometric security represents a significant advancement in authentication technology. As we move toward a more digital future, integrating these systems into everyday use will improve security and user experience. While challenges remain, the ongoing development in this field holds exciting potential for enhancing our security landscape.
For more information on biometric security and how it can protect your assets, stay tuned for our upcoming posts and updates!